All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Anti-COVID-19 Biomedicines - A Layout Proposal for Production, Storage and Transportation
Abstract
Background:
Modulation of non-specific immunity and other related activities of succulent parts of effective medicinal plants can prevent viral infections like COVID-19 through their dietary intake.
Objective:
The succulent parts of the medicinal plants with immunomodulation, anti-oxidation, anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, etc. power can be used orally in the capsular form to prevent as well as to reduce the severity of symptoms of COVID-19.
Methods:
A proposal is displayed with a detailed description of related steps like the selection of medicinal plant parts consulting related reports, collection of biomedicines, validation of efficacy, dosing, encapsulation, storage, and transportation, etc.
Results:
The succulent bio-medicines against COVID-19 can be developed and marketed following only some adoptive research.
Conclusion:
Succulent bio-medicines can be prepared and marketed for the prevention and cure of different infectious and non-infectious diseases.
1. INTRODUCTION
The novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection is causing huge morbidity and mortality in almost all the countries around the globe. The main symptoms of the disease are fever, sore throat, cough, chest pain, muscle pain, respiratory problems, headache, etc. which lead to further severity by causing respiratory insufficiency, affecting the vital organs like the heart, liver, kidney, nervous system, etc. and ultimately causing the death of many patients, particularly those having any previous co-morbidity [1].
For the diagnosis of this disease, some antigen testing procedures are available to detect the presence of the viral envelop proteins from the nasopharyngeal fluids. But the main testing procedure used for this purpose is real-time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) [2]. Other methods available are RT Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) which is based on nanotechnology [2], detection of plasmonic meta-sensors even when low-molecular-weight biomolecules are available at low densities, different modern techniques like toroidal meta-surface technology to diagnose the disease is also under study [1].
Antibodies against the COVID-19 viruses are detected from the serum mainly by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a qualitative detection of IgG or IgM antibodies raised against the virus by the infected individuals at different time intervals [2].
Vaccination of the people and use of medicines like corticosteroids, antivirals, antibiotics, etc. are the procedures used presently to control the pandemic. Many synthetic drugs are tested for their efficacy and later rejected from the treatment schedule for not getting desirable or satisfactory effects [3].
The idea of using succulent parts of medicinal plants as bio-medicine is perhaps reverse to the concept of Modern medicine, which generally targets the development of the medicines synthetically. The contemporary Ayurvedic medicines available in the market and almost all other medicines prepared using herbal sources use mostly the dried parts of medicinal plants. Drying and all other processing procedures generally negatively affect the bio-availability of the phytoconstituents actually present in any part of a living plant, both in consideration of number, quantity and quality [4, 5]. Boiling of the medicinal plant parts to prepare decoctions has the same type of limitations [5-7].
For initiation and maintenance of different infectious as well as non-infectious diseases, the effect of lifestyle-related factors can never be neglected. The ‘permitted’ synthetic chemicals and known toxic chemicals of different names and categories that enter inside our body system may act cumulatively and so can reduce the normal disease preventive power of the body. That can accelerate or trigger the genetic predisposition and/ or catching as well as the spread of different diseases [6, 7].
Removal of cause and curing of the effects is the target of all therapies. For COVID-19, a viral disease, the same can be considered as true. The succulent biomedicines can be a good option for the prevention of that disease, reduction of disease symptoms, and restoration of health after recovery. So, they can act as curative in one hand and as masking agents on untoward effects of genetic predisposition in the other. Diet is also one important factor. Nutrients available to the body from the diet in pre-disease, disease, and post disease conditions of COVID-19 can also influence the disease condition [8].
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
The present research deals with the framing of a system to produce and use succulent biomedicines to control COVID-19 and alike diseases. Under the methodology of the research, the following points are covered.
i) Identification of the therapeutic concepts for the control of the disease by use of succulent biomedicines.
ii) Survey of the medicinal plants having report/s to influence COVID–19 and alike diseases and/ or symptoms.
iii) Selection of some plants for use of their parts at therapeutic purposes to prevent the disease.
iv) Chalking out of different steps for production and use of the biomedicines.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Identification of the Therapeutic Concepts for Control of the Disease by use of Succulent Biomedicines
3.1.1. Concept of Succulent Biomedicines and their use to Control Diseases like COVID-19
The succulent biomedicines can perform their activities inside the body system in different ways. They can act directly on the invading microorganisms, as on their growth, multiplication, and spread. They can also work by modulating different arms of the immunity system of the body [9]. Prevention of catching the infections, reduction of severity of the symptoms, and triggering or masking of the genetic predisposition of an individual may have a tremendous effect on the overall disease . The concept of the use of succulent biomedicines to control different diseases is having some other important areas that require separate analysis to determine the possible effects of these medicines on the overall physiological system [9].
3.1.2. The Cumulative Effect Concept
Contemporary researches performed for the validation of effects of plant parts as medicine are mainly or solely target identification of the active principles to synthesize them chemically to market as medicines. Such research is linked with the development of new drugs for Modern medicine.
Almost all the contemporary Alternative Healthcare Systems related with the use of part of herbs directly as medicines generally use the dried plant parts or their chemical extracts or decoctions, singly or at poly-herbal formulations.
Every medicinal plant part contains thousands of phytochemicals. In the succulent condition, all of them get the opportunity to show their activity together. But many phytochemicals of the succulent parts of medicinal plants are definitely absent or reduced in quantity in the dry form or any other processed form due to evaporation and chemical changes related to the drying or boiling procedures. In the solvent extracted portions of the dry plant parts (performed in contemporary research for drug development), only a portion of the phytoconstituents present in the dry part of the medicinal plants is extracted. Therefore, we cannot get any idea about the lost phytochemicals which were actually present in the succulent parts of plants through contemporary methods. But those may have some important effects on our health (as fruits are eaten in succulent condition to get maximum benefits) [7, 10].
The succulent bio-medicines are not having any such limitations, as they can show the cumulative effect of all phytochemicals present in the parts of medicinal plants.
3.1.3. Modulation of Non-specific Immunity
The succulent bio-medicines are having Immuno-modulation, Anti-oxidation, Antiviral and/or many other related effects. They can exert such effects through the diverse number of phytochemicals present among them.
3.1.3.1. Anti-Oxidation Activity of Plant Medicines
Nature gifted us many antioxidants in different fruits and vegetables, spices, and in many medicinal plants at their succulent stage. Along with drying, frying, and boiling at high temperatures, many of them reduce in quantity to a large extent.
Oxygen acts as the terminal acceptor of the electron during aerobic metabolism. That oxygen then splits into single atoms with an unpaired electron and thus seeks another electron to be paired. Such single atom oxygen is termed as free radicals and the scavenging activity of these free radicals can cause many detrimental health effects inside the body. If such activities are not controlled by the supply of antioxidants, damage or disruption of different cellular bio-molecules will be there through the production of different Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) [11]. By incurring negative influences on different important aspects of the body like signal transduction system of the body, expression of the gene of individuals, inactivating different receptors, influencing the immune system, acting on nuclear transcription factors, aging, cytotoxic activities, etc., these can cause severe harmful effects in the overall body system which may lead to easy transmission of infections and showing more severity in the expression of disease symptoms [12, 13].
The antioxidants can prevent these detrimental processes or can slow down these by removing the free radicals, thus can protect us from various diseases.
Carotenoids (nearly 1000 are known) and Phenolic compounds (identified over 400 flavonoids, more than 8000 plant phenols, Benzoic acid derivatives; proanthocyanins, stilbenes, coumarins, lignans, lignin, etc.) are some well-known antioxidants [12, 14].
The dietary intake of a single antioxidant even in large quantity is not profitable. Regular intake of different antioxidants is the only way to get the best benefit from them [12].
Many antioxidants are present in edible vegetable items (like succulent fruits, vegetables, etc.). Selective use of succulent biomedicines can supply particular antioxidants to control the targeted adverse effects and reactions of the oxidants inside the body [10].
3.1.3.2. Immunomodulation Activities
The stimulatory or suppressive activities of the dietary supplied phytochemicals on the immunity system of the body can influence the health status of an individual to a large extent [15]. Such modulation of immunity power can increase the body resistance by influencing the cells and the mediators of the system and can prevent various infections. An increase of the abilities like oxidative activities of blood neutrophils, phagocytic power of the cells of microphase lineage, activities of the cytotoxic T lymphocytes to destroy virus-infected cells or cancer cells, etc. can assist in such works. Control of excessive activities of some cells is also very important for the prevention and cure of dangerous diseases like hypersensitivity diseases [9, 16].
The succulent biomedicines can act at various different areas of the immune system. These include antigen recognition and phagocytosis, lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation, synthesis of antibodies, interactions of antibodies with antigen, the release of biochemical mediators of the immune response, control of autoimmune diseases, modification of target tissue response and target effector organs, influence on apoptosis by affecting the programmed cell death, influence on the complement system of the body etc [17-19].
3.1.4. Antiviral Effects
Metabolites of the dietary taken succulent biomedicines can work against invading viruses in various ways. It may be through modulation of different arms and parameters of immunity system of the body or by incurring direct effects on replication and spread of the virus, expression of the disease symptoms, effect on the killing of virus-infected cells by the Cytotoxic T lymphocytes etc [9].
3.1.5. Other Related Effects
Activities as control of different co-morbidities like diabetes, hypertension, arteriosclerosis, obesity, improper liver or kidney function, problems of the gastrointestinal system, etc. can definitely influence the body immunity and can also affect the catching of infections and development of diseases like COVID-19. Many succulent biomedicines are having additional powers to control such co-morbidities and also cure the related problems [9].
3.1.6. Use as Some Preventive Medicines
The succulent biomedicines can also supply many additional benefits in different health problems. These can be used as preventive medicines for different infections at the individual level, for the susceptible population in epidemic conditions, during as well as after recovery of many infections. They can be effectively used along with vaccination and also during allopathic medication of devastating diseases like cancers. To modulate overall body immunity, these can also be used for a few days before and after any major surgery.
Many reports are available for possible health impacts of herbal medicines as anti-aging [20], hepatoprotective [21], radioprotective [22], etc. In many cases, such effects are interlinked and one succulent biomedicine can show more than one type of positive health effect [9].
3.1.7. Negligible Chance of Development of Resistance by the Invading Organisms
As the number of total phytoconstituents even in a single bio-medicine maybe some thousands in number (maybe multiplied to some folds when a few such medicines are used together), and they are supposed to act on the different receptors of the body system and can also modulate the synthesis and activities of different cytokines following different ways along with other effects (mechanism of actions), so there may be practically no chance for the building of resistance against all of them by the organisms like COVID-19 virus [9].
3.1.8. Supply of Important Micronutrients
The succulent bio-medicines can also supply almost all-important natural micronutrients (Vitamins, Minerals, etc.) along with other phytochemicals, which are generally absent in processed and fried foods. People of contemporary generations are adopted in eating such foods. This may be an additional benefit of the use of such bio-medicines to all of them [7].
3.2. Survey of the Medicinal Plants having Report to Influence COVID–19 and alike Diseases and/ or Symptoms
3.2.1. Parameters for Selection of Medicinal Plants having the Power to Control COVID–19
Succulent parts of medicinal plants can work against the COVID-19 virus in various ways together. The abilities like modification of various parameters related with Innate or Non-specific immunity - antioxidation, immunomodulation, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic, etc. activities; protective actions on the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, etc. are important. Other activities like anti-diabetic, anti-cholesteric, hepato-protective, reno-protective, etc. actions are also not less important. Such activities of that type of plant-derived bio-medicines are considered along with direct antiviral and other antimicrobial effects [5, 7, 9]. One important difference between such succulent bio-medicines with Modern medicines is that even a single bio-medicine may show many of these stated activities together. It can be easily imagined that the cumulative activities of a few of such bio-medicines may be very diverse and strong to bring desirable effects (Fig. 1).
3.2.2. Identification of the Medicinal Plants with Anti-COVID-19 Activities
Many articles are surveyed for searching of medicinal plants with desired activities. Some reports are available with possible antiviral activities of the medicinal plant parts. The name of 1060 plants having a report of controlling and combating infectious diseases was a good source article for the collection of related plants [23]. The name of 78 plants with related activities is described in another publication [10]. Another list of 130 plants with reports of immunomodulation to control and cure diseases [9] is also considered.
3.3. Selection of some Plants for use of their Parts at Therapeutic Purposes to Prevent the Disease
3.3.1. Selection of the Medicinal Plants
Many plants are having the power to act directly or indirectly against initiation, spread, and expression of disease symptoms of viral infections like COVID-19. Among such plants, many plants are well known to the research community for years and there are many plants that are already in use by the common people at different forms in many other purposes, but generally not used orally in succulent form as some medicines (Fig. 2).
Considering all the available resources, 25 plants are selected for the preparation of succulent biomedicines from them at the present primary level effort with an expectation of nil or negligible toxicity in their oral therapeutic doses and available study reports of their efficacy possibly related with COVID-19. As it is a proposal for the development of biomedicines at the primary level, only such a small number of plants are considered. However, each and every medicinal plant having a report of related efficacies may be considered for the same type of study in the future.
The already identified related effects of the selected medicinal plants are added for each of these 25 medicinal plants in the following section. As the study report on succulent parts of medicinal plants or their juices/ seed powders etc. is scarce, the available records, mainly the activity study of the solvent extracted portion of dry plant parts or isolated phytochemicals or the previous reports of the use of medicinal plant parts for related purposes are added for each medicinal plant (Fig. 3).
3.3.2. Indication, Doses, etc.
The proposed indication, doses, etc. added against each plant are just to express some idea about these points and in no case, these are to be considered as final. The combinational use schedule of the biomedicines for preventive, curative, as well as at post disease conditions also requires some adoptive research before finalization (Figs. 4 and 5).
3.3.3. List of Medicinal Plants having the Ability to Control COVID-19
The selected medicinal plants with the ability to control viral infections like COVID-19 are listed. The name of the plants with Family, previous related research findings, and other details are collected and added for each plant. The name of the plants is added following the order of English letters. Photographs of the plants are added in Fig. (1).
3.3.3.1. Adhatoda Vasica Nees
Family: Acanthaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [24-26], Immunomodulant [26-28], Antiviral [26, 29, 30], Antimicrobial [24, 26, 31], Cardioprotective [26, 31], Anti-cholinesterase [31], Bronchodilator [32], Anti-inflammatory [26, 31], Hepatoprotective, Antidiabetic, Thrombolytic [26].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 3 -7 days in a week as per requirement.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.2. Allium Sativum L.
Family: Amaryllidaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [33-35], Immunomodulant [36-38], Anticancer [35, 37, 39], Antiviral [36, 40, 41], Anti-inflammatory, Anti-microbial, Cardioprotective [35-37], control Respiratory infections, Tuberculosis, Duodenal ulcer [42].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent bulb.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/pressure extract.
(c) Use: Daily.
(d) Proposed dose: 4-6 grams bulb paste for adults.
3.3.3.3. Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees
Family: Acanthaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [43-45], Immunomodulant [46-48], Antiviral [47, 49, 50], Anticancer [44], Anti-Inflammatory [44, 48], Hepatoprotective, Antimicrobial, Antipyretic, Analgesic, Antimalarial, Antihyperglycemic, positive effects on cardiovascular diseases, inhibitory effects on Platelet aggregation [44]; in Influenza, Bronchitis [42].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 1-2 days in a week, preferably at empty stomach (morning), abstaining foods for next one hour.
(d) Proposed dose: 2-3 grams of leaves per dose for adults.
3.3.3.4. Azadirachta indica A. Juss
Family: Meliaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [51-53], Immunomodulant [51, 54, 55], Antiviral [51, 56, 57]; Antibacterial, Antifungal, Anti-inflammatory [51].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 3-5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.5. Chlorophytum borivilianum Santapau & R.R. Fern
Family: Asparagaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [58-60], Immunomodulant [61-63], Antiviral [64], Anticancer [60, 63], Antidiabetic [60, 61, 63], Antimicrobial [60, 63], Anti-inflammatory [58], Analgesic [60, 61], Antistress [60, 61, 63], Hyper-cholesteraemic [60, 61], Antiulcer [60, 63], Aphrodisiac [60, 61, 63].
Indications:
(d) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent root.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 3-5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 10-15 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.6. Citrous limon
Family: Rutaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [65-67], Antiviral and Antimicrobial [66, 68, 69], Immunomodulant [70, 71], Anti-inflammatory [66, 68], Anticancer [66, 68, 72], Anti-allergic [66], Hepato-regenerating effect [66, 73], Antidiabetic [66, 74]; having various positive effects on Cardio-vascular Respiratory, Nervous and Skeletal system [66]; can bring down Fever and balance pH [72].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Fruit.
(b) Proposed form of use: Pressure extracts (Juice).
(c) Use: Daily in morning, mixing with lukewarm water.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 50 - 100 drops for adults.
3.3.3.7. Curcuma longa L.
Family: Zingiberaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [75-77], Immunomodulant [78-80], Anticancer [77, 81], Antiviral [82-84]; Anti-inflammatory, Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antidiabetic, Anticoagulant, Cardiovascular protective, Hepatoprotective [77].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent rhizome.
(b) Proposed form of use: Pulp/pressure extract.
(c) Use: May be daily in the morning at an empty stomach for 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 5-10 grams for adults.
3.3.3.8. Daucus carota L
Family: Apiaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [85-87], Anticancer [86, 87], Immunomodulant [86], Antiviral [88, 89], seed antiviral [90]; Antimicrobial, Smooth muscle relaxant [91]; Anti-diabetic, Cholesterol and Cardiovascular disease protecting, Anti-hypertensive, Hepatoprotective, Reno-protective etc [86, 87].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent root.
(b) Proposed form of use: Pulp/pressure extract.
(c) Use: For 5-7 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 5-10 grams for adults.
3.3.3.9. Emblica officinalis Gaertn
Family: Phyllanthaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [92-94], Immunomodulant [92-94], Antiviral [94-96], Anticarcinogenic [92, 93, 95], Antipyretic, in Cold and Fever, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Antitussive, Antiatherogenic, Adaptogenic, Cardioprotective, Gastroprotective, Anti-anemic, Anti-hypercholesterolemic, Antidiarrheal, Anti-atherosclerotic, Hepatoprotective, Nephroprotective, Neuroprotective properties [92, 93], Antimicrobial, Antidiabetic, Antiulcerogenic [93, 95].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent fruit.
(b) Proposed form of use: Pulp/pressure extract.
(c) Use: Daily.
(d) Proposed dose: 5-6 grams of pulp for adults.
3.3.3.10. Hibiscus sabdariffa L.
Family: Malvaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [96-99], Immunomodulant [100-102], Antiviral [103-105], Anticancer, Hepatoprotective, Nephroprotective, Antibacterial, Renal/Diuretic effect, Antipyretic, Anti-inflammatory, Anti-cholesterol, Anti-diabetic, Anti-hypertensive, Anti-obesity, Anti-anemic activities [98].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaves and petals over fruits.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/pressure extract.
(c) Use: Daily in the afternoon.
(d) Proposed dose: Extract of 5-10 leaves per dose for adults.
3.3.3.11. Moringa oleifera Lam.
Family: Moringaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant (leaf- [106-108]; pod - [109]), Immunomodulant (leaf - [110-112]; flower - [113]), Antiviral (leaf - [57, 114, 115]; seed - [116]), Anti-inflammatory (leaf- [108]), Anti-diabetes (pod- [109]); Leaf in High blood pressure, root as Antimicrobial and as Preservative [113].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Leaf and/or flower.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 5-6 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.12. Nigella sativa L.
Family: Ranunculaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [117-119], Immunomodulant [117, 120, 121], Antiviral [122-124], Anticancer [117, 125, 126], Hepatoprotective [117, 127, 128], Antidiabetic, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Antimicrobial, Spasmolytic, Bronchodilator, Anti-hypertensive, Renal protective [117].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Seed.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ powder.
(c) Use: 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.13. Ocimum sanctum L.
Family: Lamiaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [129-131], Immunomodulant [132-134], Antiviral [135-137]; in Influenza, Common cold, Cough, Headache, Fever, Bronchitis, Asthma, Hepatic diseases, Fatigue [138]; Hypoglycemic, Hypolipidemic effects [129].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Pressure extract.
(c) Use: In the morning.
(d) Proposed dose: Extract of 10 - 20 leaves.
3.3.3.14. Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr.
Family: Myrtaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [139-141], Immunomodulant [142-144], Anticancer [139, 142, 144], Antiviral [145], Antidiabetic [139], Antimicrobial [139, 141, 142]; Hypotensive, Anti-neuralgic, Analgesic [142].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Dry berries.
(b) Proposed form of use: Powder.
(c) Use: 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.15. Piper longum L.
Family: Piperaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [146-148], Immunomodulant [148-150], Antiviral [150], Anticancer/ Anti-tumor [148, 150, 151], Hepatoprotective [148-150], Antidiabetic [148], Antimicrobial, Antiplatelet, Antihyperlipidemic, Analgesic, induce Coronary vasodilation, Cardioprotective; act to correct chronic Bronchitis, Asthma, viral Hepatitis, Respiratory infections [149, 150], diseases of the Respiratory tract [42].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Berries.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/pressure extract.
(c) Use: Daily in the afternoon for 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 4-6 grams for adults.
3.3.3.16. Piper nigrum L.
Family: Piperaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [152-154], Immunomodulant [154-156], Antiviral [151, 157, 158], Anticancer [153, 151, 154], Hepatoprotective [153, 154], Antihypertensive, Antiplatelet, Anti-asthmatics, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Anti-diarrheal, Antispasmodic, Antidepressants, Anticonvulsant, Antibacterial, Antifungal [153], in Cough, Sinusitis [113].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Dry seed.
(b) Proposed form of use: Powder.
(c) Use: At afternoon for 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: 5-6 seeds per dose in adults.
3.3.3.17. Rosmarinus officinalis L.
Family: Lamiaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [159-161], Immunomodulant [162-164], Antiviral [114, 165], Antimicrobial [159], Hepatoprotective [160] etc.
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.18. Taraxacum Officinale (L.) Weber ex F.H. Wigg.
Family: Asteraceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [166-168], Immunomodulant [169-171], Antiviral [172-174], Anticancer [166, 175], Antidiabetic [171], Anti-lipidemic [167], Anti-inflammatory, Diuretic, Analgesic, Anti-hyperglycemic, Anticoagulatory, Prebiotic effects; Spleen and Liver protective [166]; active in Obesity, Hepatitis, Arthritis, Cardiovascular diseases [175].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Whole plant.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.19. Terminalia Chebula Retz.
Family: Combretaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [176-178], Immunomodulant [179-181], Antiviral [182-184], Anticancer [185], Analgesic [178]; Antimicrobial, Antidiabetic. Cardioprotective, Hypo-cholesterolemic, Adaptogenic and Anti-anaphylactic, Hepatoprotective [185]; in Kidney and Liver problems; having Antitussive, Homeostatic, Diuretic, Laxative effects [181].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Dried fruit.
(b) Proposed form of use: Powder of the dried pulp.
(c) Use: 3-4 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.20. Thymus Vulgaris L.
Family: Lamiaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [186-188], Immunomodulant [189-191], Antiviral [192-194], Antimicrobial [188, 195] etc.
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 3 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.21. Tinospora Cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers.
Family: Menispermaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [196-198] Immunomodulant [199-201], Antiviral [202, 203], in Kidney and Liver problems, having Antitussive, Cardiotonic, Homeostatic, Diuretic etc. effects [181].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent stem.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 3-5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.22. Vaccinium Corymbosum L.
Family: Ericaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [204-206], Immunomodulant [206, 207], Antiviral [208], Anticancer [208], Anti- diabetes [206, 208], Anti-inflammatory [204, 206], active against Circulatory disorder [208], Hypercholesterolemia and Hypertension [206].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Ripe fruit
(b) Proposed form of use: Pulp paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: May be daily.
(d) Proposed dose: May be 20-25 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.23. Vernonia amygdalina Delile.
Family: Asteraceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [209-211], Immunomodulant [212-214], Antiviral [215, 216], Anticancer [210, 215, 217]; Anti-diabetic, Liver protective, Anti-allergic, Anti-inflammatory, Antimicrobial, Anti-malaria, Anti-leukemia [215, 217].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent shoot and leaf.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste/ pressure extract.
(c) Use: 3-4 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 3-5 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.24. Withania Somnifera (L.) Dunal.
Family: Solanaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [218-220], Immunomodulant [221-223], Antiviral [224-226], Anticancer [221, 227], Antimicrobial [218, 221], Anti-inflammatory [221, 228]; Hypolipidemic, Cardiovascular protection, Anti-stress, assist in Hematopoiesis [221].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Root.
(b) Proposed form of use: Paste.
(c) Use: 3-5 days in a week.
(d) Proposed dose: May be within 2-3 grams per dose for adults.
3.3.3.25. Zingiber officinale Roscoe.
Family: Zingiberaceae
Related previous reports:
Antioxidant [42, 229, 230], Immunostimulant [231-233], Anticancer [234-236], Antiviral [237-239], Hepatoprotective [240], Respiratory protective, Anti-inflammatory, Antidiabetic, Antimicrobial, Neuroprotective, Cardiovascular protective, Anti-obesity, Antinausea, Antiemetic activities [230].
Indications:
(a) Part of the plant to be used: Succulent rhizome.
(b) Proposed form of use: Pulp/pressure extract.
(c) Use: Normal - once daily for 3 days in a week; thrice daily in patients with involvement of respiratory organs.
(d) Proposed dose: 2-3 grams pulp per dose for adults.
3.4. Chalking out of Different Steps for Production and use of the Biomedicines
Different steps are studied for validation of reported activities, collection of the proper parts of the medicinal plants, production of succulent biomedicines from them and their transportation up to the patient level.
3.4.1. Validation of Claimed Activities
For validation of the reported activities of the medicinal plants to control viral infections like COVID-19, the in vivo studies of the succulent parts of the medicinal plants may be given preference.
There are many reports available regarding the presence of the identifiable phytochemicals in the solvent extracted section of the dry parts of the listed medicinal plants. Studies on the effects of the identified phytochemicals are generally performed in contemporary phytomedicine research throughout the globe for identification of active principle/s principally with an intention of synthetically producing them to market as Modern medicine.
The present concept related with the novel proposal of development of succulent biomedicines is out of that contemporary research idea.
As per the new concept, related studies to find out and/or prove the effects and abilities of the succulent parts of the reported medicinal plants with an intention to market them directly as medicines (rather than identification of phytochemicals present among them) may be given preference. The logic behind the present concept is that many phytochemicals may be volatile in nature or may be present in very minute, undetectable amounts in the succulent bio-medicines (and may be absent in diluents-extracted sections of dry medicinal plant parts). But these may have very good effects on our health. So, it will be a better option to study the cumulative effects (total effects) of all phytoconstituents present in the succulent bio-medicines preferably in vivo [7].
The already developed and available techniques/procedures to perform the related studies in contemporary research may be adopted for that purpose also with some required modification/s.
3.4.1.1. Constraints in the Validation Process and the Possible Solutions
Identification of the mechanism of actions of medicines of synthetic or semi-synthetic origin used in Modern medicine is presently at a more or less established stage due to intense study performed by many dedicated scientists and research workers and addition, alteration, and other modifications of the ideas and procedures continuously by them.
But it is not so easy to identify and establish the mechanism of actions of the succulent biomedicines even by using the modern techniques.
There are several reasons behind it.
(i) The medicines of synthetic origin (used in Modern medicine - the ‘drugs’) act as a single molecule most of the time. The succulent herbs may contain several molecules; some of them are so negligible in amount (though may be a source of very strong effects) that they may remain below the level of detection even during use of the latest techniques available in modern analytical science.
(ii) It is easy to follow a single drug from its ingestion up to the excretion from the body system. But it cannot be said for succulent bio-medicines, as their activities are like the ingested succulent fruits.
(iii) Involvement of receptors of the body system may be far more complex in the activity study of biomedicines due to the same reason of presence of a huge number of phytochemicals of different amounts.
(iv) The metabolic products of the huge number of phytochemicals present in a single bio-medicine may be very diverse and so it may be very difficult to identify all of them and then to perform further studies on them.
(v) The concept of study of synthetic medicines may not be applicable to study the biomedicines in many cases due to the fact that some components of the biomedicines may not show their effect instantly. They may act slow or very slow in our system.
(vi) As the metabolic products of the phyto-constituents taken orally through succulent bio-medicines (like the edible fruits taken at succulent stage) work actually inside our body system, so emphasis may be given to the effect of metabolic products of such medicines, not on the phytochemicals isolated in the laboratories only.
(vii) Positive actions of some components of succulent bio-medicines may be compared with the detrimental effects of the xenobiotic residues and/or adulterated toxic chemicals enter our body for their activity mechanism, as both of these groups can act very slowly and actually the cumulative effect of all of them is expressed ultimately.
So, the validation processes for reported activities of succulent bio-medicines need to be different from those applied in Modern medicine.
The presently available techniques/ procedures directed towards the study of activities of single molecules may be modified with a direction to study the cumulative action of all the phytochemicals present in the bio-medicines, if required.
Shifting to a new concept can solve these problems, as displayed in Fig. (2).
3.4.1.2. Study for Toxicity and Dose
It can be performed following conventional procedures already developed and followed in Modern Medicine with some modifications, if required.
For succulent biomedicines, one important point related to the calculation of doses is that the availability of effective phytoconstituents is not constant in the raw materials obtained from different sources/ times. It is variable with the factors like the type of soil, stage of growth of the plant, temperature, humidity, and other related factors of the area during cultivation of the plant etc.
The presence of main phytoconstituents in each batch of raw materials may be matched with a standard chart (can be prepared using available resources) before calculation of individual doses.
All the selected twenty-five plants are expected to have no toxicity at therapeutic doses. However, among all the bio-medicines listed, some are regularly consumed by many people in different purposes (plant numbers 2, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 19, 22, 25). So, these perhaps do not require any vigorous study of toxicity. Other plants may require to some extent rigid toxicity study.
3.4.2. Production of Succulent Bio-medicines
Different steps related to the production of succulent biomedicines for COVID-19 is discussed in the following paragraphs. A flow diagram of all the related procedures is displayed in Fig. (3).
3.4.2.1. Collection of Materials
Cultivation of the medicinal plants may be arranged at their natural or near-natural soil and environment. It will be the best option to perform Organic Farming of these plants. Adulteration of plant parts by the supplier may be a dangerous problem, so proper care should be taken in the whole process, from the cultivation of plants and collection of raw materials up to their transportation to the industry [5, 7].
The plant materials may be collected by hands covered by sterile gloves or by use of any mechanical means. Then the materials may be washed by germ-free water and then by distilled water. These may be soaked in salt, vinegar, baking soda, and lemon juice prior to preservation as per specific requirements [241].
Washing by of 70% Ethyl alcohol may be performed to control the vegetative microorganisms of the surface of the plant parts [7].
The surface of the fruit, root, leaves, etc. may require mechanical removal of adhered dust and other materials. Sterile absorbable cotton soaked with 70% Ethyl alcohol may be used to clean them. Potassium permanganate, Alum, Sodium bicarbonate, Lime water, etc. chemicals may be used for such primary washing as per specific requirements [7].
After such washing, a final thorough washing by distilled water (of normal room temperature, lukewarm temperature, or hot water as per the requirement) may be required. Then the materials may be kept under the shade with the flow of dust-free and germ-free air (as performed in laminar flow system) for removal of adhered water droplets.
3.4.2.2. Collection of Cut Pieces, Pastes and Juices from Succulent Plant Parts
The external cover of the cleaned plant parts (of fruits, roots, stems, etc.) may be removed by proper sterile sharp instruments or by other efficient mechanical means. The materials may be divided into some pieces by sterile instruments. As per the requirements, removal of seed, pulp, hard parts, etc. maybe performed in a germ-free environment.
The materials may be converted to paste by any mechanical means using proper instruments as performed on a small scale by Mixture and Grinder. The juices may be extracted out by applying mechanical pressure using proper instruments. Filtration of the materials may be required in some cases. The cut pieces, pulps, juices, etc. may be kept at low temperatures (as 0°C) or at freezing temperatures (below 0°C) before use at the next specific purpose/s [7].
3.4.2.3. Conversion of Dry Seeds to Powder
The dry seeds or dry fruits may be converted to fine dust by taking appropriate machinery assistance as per the requirements.
3.4.2.4. Individual Dosing of the Medicines and their use
(i) Proposed pattern of use of medicines: Some medicines may be used almost in the routine purpose for the modulation of body immunity and other activities. Some others may be used in diseased conditions and some others for specialized purposes. Preparation of indications for use of the bio-medicines also requires some study before standardization.
(ii) Pattern of dosing of bio-medicines: In the list of twenty-five selected plants, proposed use pattern and dosing are added. The approximate weight of the raw bio-material (leaf, pulp, etc.) is added there. As these dosing etc. are all speculative in nature, some adoptive research is required in these areas also. Research is also required for the use of medicines for definite purposes - as some may be used regularly by immune-compromised patients/ elderly patients, some during pandemics, etc.
3.4.3. Preservation of the Succulent Bio-medicines
Man uses succulent part of the plants (fruits, leaves, roots, etc. of many plants) as some source of many important nutrients, micronutrients, or medicines from a very ancient day. Use of dry parts of the plants at required purposes were developed due to many reasons, perhaps mainly for non-availability of them throughout the year and for their spoilage during storage and transportation.
Afterward, a technique for the addition of different germicidal chemicals in the extracted juices of fruits, etc., and liquid/ semisolid/ tablet presentation of the dry powders of the medicinal plant parts after mixing with some germicides was developed to overcome these problems (the preservatives). Along with these, some other chemicals were also added without any scientific reason, perhaps just to attract the consumers (the added flavor, color, etc.). The cumulative effects of all these chemicals in continuous use cannot be considered as undoubtedly safe for our health [7].
In the field of herbal medicines, the dry parts of the medicinal plants are mainly used. The dry powders are used in liquid form after mixing with ethyl alcohol and/ or some other germicidal materials. Other forms like semisolid or tablet presentation of the dry powders of the medicinal plant parts with or without vehicle materials were also in practice. Boiling of one or a few herbal plant parts/s to prepare decoction is another practice.
In all such cases, the main reasons behind such presentations were seasonal availability and spoilage during storage of the plant-derived succulent bio-materials.
Now, the time has come to stop the unhealthy practices of the addition of harmful chemicals as well as to stop the wastage of important phytochemicals inside the herbal medicines.
At the present stage of civilization, the ancient problems of storage and transportation of succulent bio-materials are not at all relevant. So, we do not need the addition of any synthetic chemical to overcome the ancient problems. We are also not forced to use only the dry plant parts or their chemical extracted portions to overcome the old problems, as we are having much more efficient alternatives [7].
As per the present concept, chemical/ synthetic preservatives should not get any chance of incorporation in the proposed succulent bio-medicines. As these medicines are to be encapsulated and transported through the cold chain, the chance of multiplication of microorganisms (if present) will be very less. However, if any such requirement is felt, only preservatives of natural origin may be considered for use.
3.4.3.1. The Bio-preservatives
Several bio-preservatives are identified by many scientists, but their efficacies are to be tested in the preservation of succulent bio-medicines or bio-materials.
Essential oils of Onion, Clove, Garlic, Cinnamon, Coriander, Mount Atlas mastic, Mint Thyme, Zizyphus jujuba, Artemisia anomala, Ginger oil and Callistemon lanceolatus are advocated by Miguel et al. as bio preservatives [242]. Essential oils of Basil, Oregano, Rosemary, Sage, Thyme, Coriander, Allspice, Cinnamon, Clove, Mustard, Nutmeg, Vanilla, Bergamot, Eucalyptus, and Lemon are listed as bio- preservative by Ebrahami et al. [243]. But detailed descriptions of various herbs, herb compounds, spices, essential oils of plants, natural substances, animal, bird and insect origin products, etc. are described and discussed in one recent book [7].
The concentrated juice or the essential oil derived from the same medicinal plant of original succulent bio-medicine may be the best choice (as the essential oil of Azadirachta indica leaves may be used to cover the frozen Azadirachta indica leaf juice or pulp for preservation, if it can perform the function). These may play the role of covering bio-preservative of the succulent bio-medicines most efficiently (Figs. 2 and 3). The next preference may be given to honey and then other bio-preservatives.
3.4.4. Encapsulation of the Biomedicines
3.4.4.1. Encapsulating Materials of Biological Origin
Many materials of biological origin may be considered for their efficacy of encapsulation. Like the bio-preservatives, their efficacy in the present purpose is to be tested. Among the plant-derived materials, plant exudates (Gum Arabic, Gum karaya, Mesquite gum); plant extracts (Galactomannans, Soluble soybean, Pectin, Cocoa butter); different Starch and Cellulose derivatives, Polysaccharides; proteins like Gluten (corn), Wheat gluten, isolates of Pea or Soy; lipids like Fatty acids/ alcohols, Glycerides, Waxes (Bee wax, Candelilla wax, Carnauba wax), Shellac resin, Phospholipids are important. Among the marine origin products, Carrageenan, Alginate; animal or microbial products like Xanthan, Gellan, Dextran, Chitosan (carbohydrate), Caseins, Collagen, Corn, Whey proteins, Gelatin (protein), etc. are important [242, 244].
Different coating techniques, their qualities, and limitations as well as various coating materials of each group require detailed analysis before finalization [7].
At the initial stage of research, collagen or a combination of collagen and cellulose (as used in a sausage casing) and soft gel capsular materials may be considered for use.
3.4.5. Important Relevant Areas Need Consideration during Finalization of the Whole Process
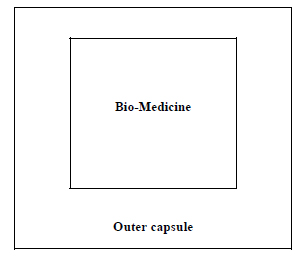
The type 1 encapsulation procedure (Fig. 4) can be applied where no bio-preservative is used. The succulent bio-medicines may be directly encapsulated to enter in the next step. The powder of the seed/ dry fruits etc. maybe directly encapsulated following that procedure.
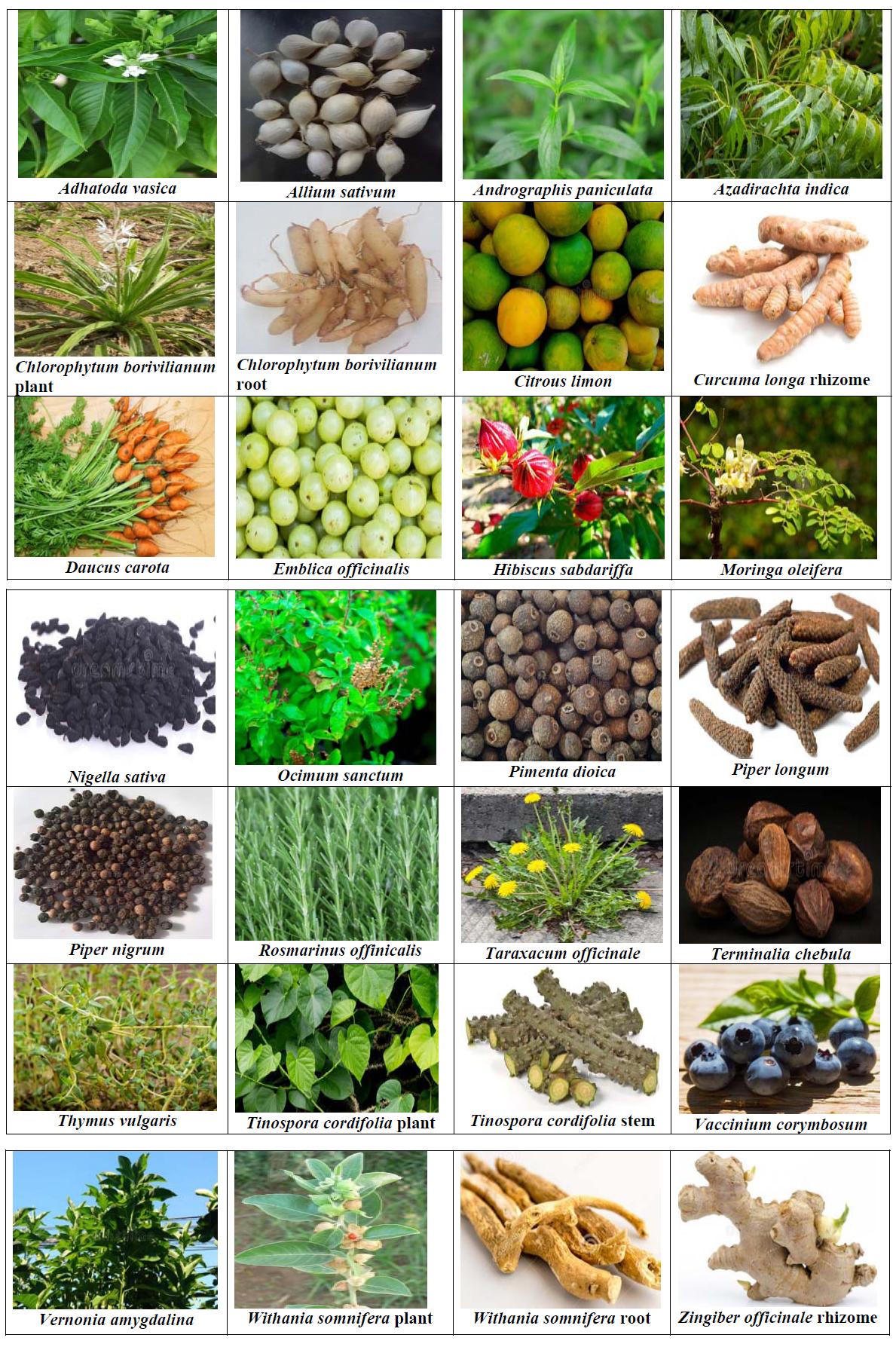

*Photographs are taken mainly from the stock photos available royalty-free from https://www.dreamstime.com/photos-images/adhatoda.html


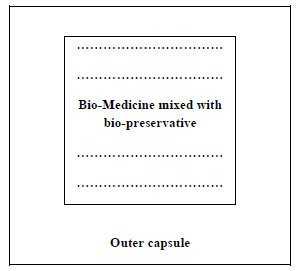
The bio-preservatives may be mixed with the bio-medicines before encapsulation following the model of type 2 (Fig. 5).
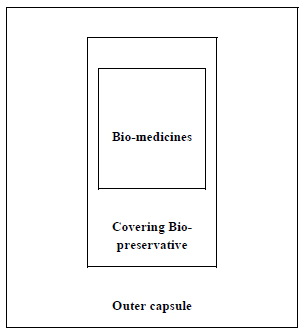
For encapsulation of the succulent bio-medicines by type 3 process, some other points are to be considered (Fig. 6).
(a) Pulp of succulent medicines or their juices may be the innermost part. That part may be made frozen before entering the next step.
(b) The previously collected juice of the same plant part of bio-medicine may be used directly or in concentrated form as the covering bio-preservative as a preferred option, if it can serve the purpose. The essential oil of the same plant part may also be used.
(c) Honey, essential oils of other plant sources, or concentrated sugary sap of some other plants may also be used as a covering preservative.
3.4.5.1. Set-up for Preparation of Bio-medicines for Packaging and Transportation
A model set up for the preparation of succulent biomedicines before packaging by stepwise freezing. Modification of this model or use of other similar setups may be performed as per the requirement.
3.4.6. Packaging of Biomedicines
The individual doses of the succulent encapsulated biomedicines may be packed singly inside small chambers of a tray or box. The tray or box should be tolerable to deep freezing and should have no toxic effect on the biomedicines kept inside them [as steel/glass etc.]. However, some tricks like the use of a bio-lubricator may be adopted for better safety of the biomedicines from the adherence with the materials of the packing box (Fig. 7).
3.4.7. Storage and Transportation of the Biomedicines
For storage and transportation of succulent biomedicines, introduction of a novel system is required to serve the required purposes. This can be developed by logical use of the available technologies to fulfill the requirements.
3.4.8. A Novel Freezing System for Storage of Succulent Bio-medicines and other Succulent Bio-Products
In order to achieve extended storage life, the succulent bio-medicines may be kept below - 23°C, as per available study reports [245].
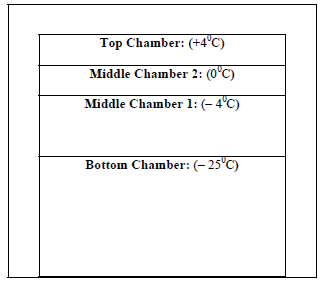
So, after production, all of the bio-medicines may be stored at some effective low temperature, maybe at - 25°C at deep freezers. During transportation to the wholesalers from the factory or during storage by the wholesalers, it may be performed at the same temperature (- 25°C). But the retail shops have to sell the products. They may be equipped with a freezing system with some special facilities as shown in Fig. (8).
The retail shopkeepers may store the bio-medicines for a longer period at the bottom chamber. The middle chamber 1 may be used as per the requirement and schedule for the sale of the medicines. The middle chamber 2 may store the medicines for a few hours.
The top chamber may be used to keep the medicines/ other succulent bioproducts for a while before delivering them directly to the consumers. This model needs detailed study before finalization.
All the above three chambers are for the storage of the medicines for a little time as per their requirement and necessity. The three upper chambers may be gradually of reduced size than the bottom chamber as per the requirements.
3.4.9. Use of Spoilage Indicator/s on the Packets of Succulent Biomedicines
The succulent bio-medicines are vulnerable to easy spoilage. The reason maybe aging, the gap in the cold chain, sabotage or there may be other previously unpredictable reason/s. There should be one easy detection procedure for the consumer/ end-user to identify the condition of the inner medicines/ products without opening the packets.
Among the available study reports on that subject, change of color of some added chemicals on the packet due to exposure of the packed materials to any environment other than the scheduled one may be considered as most important.
Electronic time-temperature indicator (eTTI) and Vaccine Vial Monitors (VVM) are two important systems to perform the work. Though the eTTI monitors can detect essentially all cold-chain breaks and can detect some other issues [246], but the VVM system may be preferred due to reasons like easy use, low cost, etc.

In the VVM system, some temperature-sensitive chemical colors are used on the packets. After exposure to a certain temperature/s for a certain period of time, the color of these chemicals' changes. Color identity is kept surrounding these chemicals. Observing the color of the surrounding area and comparing it with the color of the middle chemicals, anybody can understand the actual condition of the products kept inside the packets [7].
Such coloring materials are commonly used to determine the actual condition of the thermolabile vaccines. As these chemicals are generally used in the field of storage and transportation of vaccines, these are termed as Vaccine Vial Monitors.

3.4.9.1. Vaccine Vial Monitors
A Vaccine Vial Monitor (VVM) is a label containing a heat-sensitive material which is placed on a vaccine vial to register cumulative heat exposure over time. The combined effects of time and temperature cause the inner square of the VVM to darken, gradually and irreversibly. A direct relationship exists between the rate of color change and temperature [247].
Vaccine vial monitors are used generally to warn health care workers if a vaccine was damaged by heat. The darkened color of the monitor chemical indicates that the vaccine is no longer effective and should not be used [248].
3.4.9.2. Chemicals used in Vaccine Vial Monitors
In 1979, the World Health Organization (W.H.O.) conceived the concept of Vaccine Vial Monitor, where p-toluene sulfonate was used as the chemical for the purpose. Research, trial, and discussion were going on and in 1988, a new type of chemical, di-acetylene polymers came into the field with a better performance [249]. But the actual chemicals used presently in VVMs are not available in literature.
3.4.9.3. Reaction Rate of Vaccine Vial Monitors
From the available literature, one chart of the reaction rate of some Vaccine Vial Monitors as per their heat-stability is available. It is shown in Table 1 [250].
| Category | No. of days to end point at 37 °C |
No. of days to end point at 25 °C |
Time to end point at 5 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| VVM 30 (High stability) |
30 | 193 | More than 4 Years |
| VVM 14 (Medium stability) |
14 | 90 | More than 3 Years |
| VVM 7 (Moderate stability) |
07 | 45 | More than 2 Years |
| VVM 2 (Least stability) |
02 | Not Available | 225 days |
3.4.10. Use of Succulent Bio-medicines by the Patients
For storage of succulent bio-medicines, the health centres, hospitals, clinics, or dispensaries may be equipped with the special designed freezers (Fig. 8). But for storage of these medicines by the consumers/patients, the recommendation of the researchers is required separately for each medicine.
It is expected that the encapsulated powdered bio-medicines may tolerate to some extent higher temperatures during storage and transportation than the juices or pulps (Fig. 9). This section may also be framed as per the research results.
But in all cases, it may be the best option to swallow the capsules of succulent bio-medicines after increasing their temperature near 25 °C. The use of lukewarm water may be an option to achieve that temperature.
3.5. Requirement of Special Legislative Control on Preparation and Marketing of Succulent Bio-medicines and other alike Bio-products
All the succulent bio-medicines and other alike bio-products are prone to lose their efficacy or even conversion to some toxic materials if proper quality control measures are not taken during the preparation of the products and if any gap in the maintenance of proper cold chain arises during the longways of transportation and storage. As a part of the business competition or any other bad intentions, the medicines may be added with some toxic chemicals, some slow poisoning materials, or maybe adulterated with some health hazardous chemicals during production or in the way of their journey towards consumers.
There may be related many other problems. Compromise with the quality of biomedicines is among them.
For example - to keep production and marketing costs at a very low level to market the products at a very low cost, there may be a different compromises with the desired or directed measures by some manufacturers.
The two convenient malpractices may be the use of low-grade raw materials (without an appropriate level of phytoconstituents or the wrong plant part) and the intentional break in the cold chain.
So, many low-grade biomedicines may be sold in the market without following strict measures of manufacturing, transport, and storage of the products which may ultimately jeopardize the whole system!
To prevent all such malpractices, there should be some strong legislative control on production, transportation, storage, and marketing of these bio-medicines. As the proposed medicines are of a novel type, so the previously formulated rules and regulations may not cover all the related aspects. Specific guidelines should be imposed from the end of the competent authorities before giving any permission to manufacture and marketing of such products [7].
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the following points may be chalked out.
(1) The succulent biomedicines can act as preventive medicine for COVID 19.
(2) These also can work as medicines for the reduction of severity of disease symptoms of COVID-19.
(3) Thus the technique of immune-modulation through dilatory intake of succulent bio-medicines may be a key tool to control many other dangerous diseases and also can act to prevent any future epidemics/pandemics.
(4) The new concept can act as the basis to lead research for the development of alike procedures for prevention, control, and treatment of many other diseases of infective as well as non-infective origin.
(5) Different Bio-healthcare products may be prepared solely by different succulent parts of plants for their effective use throughout the globe in all seasons following the same procedures.
(6) Preservative and all other added chemical-free fruit pulp and fruit juices and many other food/ food products can be produced with least or zero processing and can be transported to the global consumers after adding some modifications with the basic system described.
(7) Cultivation of Medicinal plants for the production of biomedicines and their export throughout the world can involve a huge number of rural unemployed persons of the countries having plant resources. On the other hand, there are ample chances to perform agri-business through the development of a new type of agriculture and horticulture-related industries.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Not applicable.
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
Not applicable.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author confirms that this article content has no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.
